Delving into the cellular transport worksheet answer key, we embark on a scientific odyssey that unveils the intricate mechanisms governing the movement of substances across cell membranes. From passive to active transport, and from bulk transport to the significance of concentration gradients, this comprehensive guide illuminates the fundamental processes that sustain life.
As we delve deeper into the topic, we will explore the different types of cellular transport mechanisms, their importance, and the role they play in maintaining cellular homeostasis. Moreover, we will investigate the role of ATP in active transport and the various types of bulk transport, highlighting their significance in cellular function.
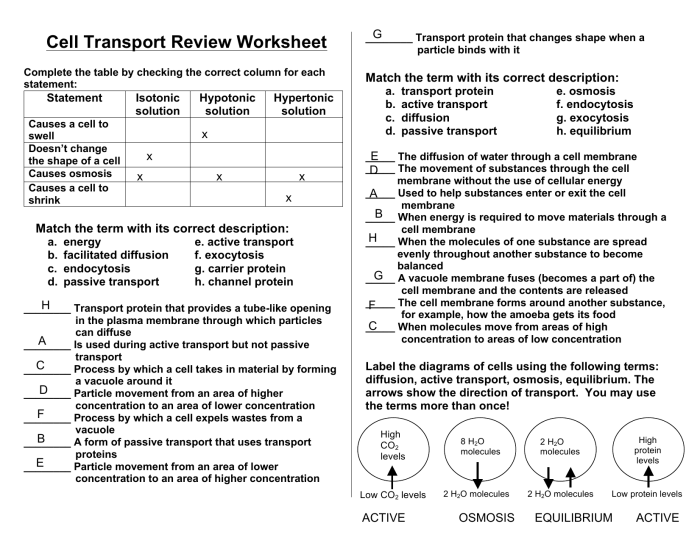
Cellular Transport Mechanisms: Cellular Transport Worksheet Answer Key
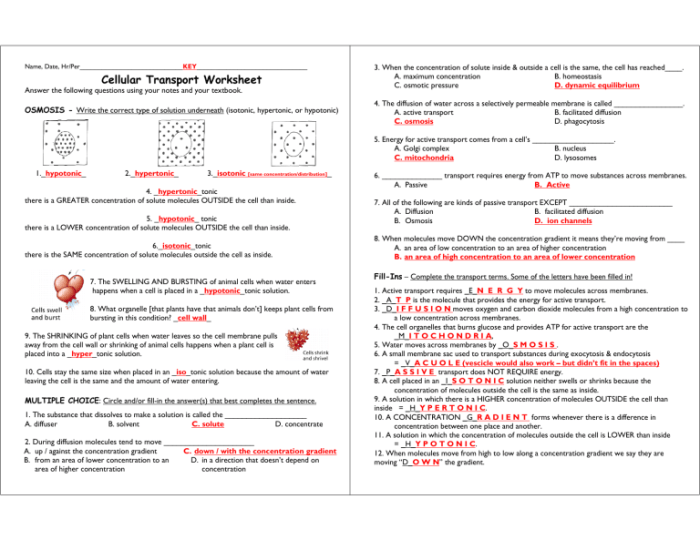
Cellular transport mechanisms are the processes by which cells transport molecules across their plasma membranes. These mechanisms are essential for the survival of cells, as they allow cells to take in nutrients and expel waste products.
There are three main types of cellular transport mechanisms: passive transport, active transport, and bulk transport.
Passive Transport
Passive transport is the movement of molecules across a plasma membrane from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration. This type of transport does not require energy.
There are two main types of passive transport: diffusion and osmosis.
- Diffusion is the movement of molecules from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration through a selectively permeable membrane.
- Osmosis is the movement of water across a selectively permeable membrane from an area of high water concentration to an area of low water concentration.
Active Transport, Cellular transport worksheet answer key
Active transport is the movement of molecules across a plasma membrane from an area of low concentration to an area of high concentration. This type of transport requires energy.
There are two main types of active transport: primary active transport and secondary active transport.
- Primary active transport is the movement of molecules across a plasma membrane against a concentration gradient using energy from ATP.
- Secondary active transport is the movement of molecules across a plasma membrane against a concentration gradient using energy from the movement of another molecule down its concentration gradient.
Bulk Transport
Bulk transport is the movement of large molecules or particles across a plasma membrane. This type of transport requires energy.
There are two main types of bulk transport: endocytosis and exocytosis.
- Endocytosis is the process by which cells take in large molecules or particles by engulfing them with their plasma membrane.
- Exocytosis is the process by which cells expel large molecules or particles by fusing their plasma membrane with the membrane of a vesicle containing the molecules or particles.
FAQ Compilation
What is the difference between passive and active transport?
Passive transport does not require energy, while active transport requires energy in the form of ATP.
What is the role of concentration gradients in passive transport?
Concentration gradients provide the driving force for passive transport, allowing substances to move from areas of high concentration to areas of low concentration.
What is the function of bulk transport?
Bulk transport allows cells to move large molecules or particles across the cell membrane.